What is Treatment-Resistant Depression and How Is It Treated?
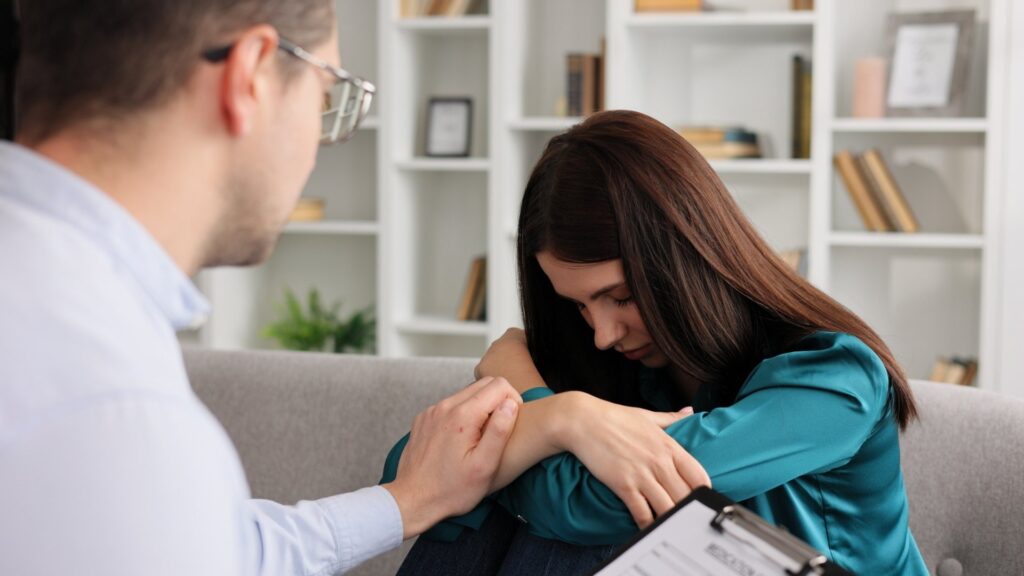

Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is a severe form of major depressive disorder (MDD) that occurs when at least two different first-line antidepressant medications fail to manage the condition during a depressive episode. This mental health condition can significantly impact a person’s life, making it challenging to perform daily tasks or maintain relationships.
Despite its name, TRD does not mean there are no treatment options available. Instead, it highlights the need for a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific needs. By reviewing the patient’s medical history and working closely with a mental health professional, individuals with TRD can explore advanced therapies like ketamine therapy and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to achieve symptom relief.
Identifying Depression Symptoms
People with treatment-resistant depression experience the same symptoms as those with major depression, but often with greater severity. Common depressive symptoms include:
Persistent sadness or depressed mood
Sleep disturbances (insomnia or hypersomnia)
Changes in appetite or weight
Loss of interest in activities once enjoyed
Fatigue or low energy
Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
Feelings of worthlessness or guilt
Suicidal ideation or thoughts of self-harm
When left untreated, these depression symptoms can worsen over time, leading to prolonged episodes and a higher risk of complications. Identifying these signs early and seeking help from a mental health professional is crucial for effective treatment.
Additionally, individuals with TRD may experience more persistent and severe symptoms, which can hinder their ability to respond positively to conventional treatments. Recognizing these patterns is essential to guide patients toward more innovative treatment methods.
Causes and Diagnosis of Treatment-Resistant Depression
Researchers are still working to understand the exact cause of TRD. However, some contributing factors include:
Chronic stress, which can alter the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. Chronic stress can worsen depression, making it more challenging to treat.
Genetic predisposition
Imbalances in brain chemistry
Underlying physical health conditions, such as thyroid disorders or chronic illnesses
Diagnosing TRD requires a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical and psychiatric history. A mental health professional will assess:
The effectiveness of past treatments, including medications and therapy
The presence of co-occurring mental health conditions
Any factors that may be influencing treatment outcomes, such as lifestyle or stressors
A comprehensive assessment often includes blood tests to rule out other physical health conditions and imaging studies to understand brain function. These steps ensure that the treatment plan addresses all aspects of the individual’s health, allowing for a more targeted approach to managing TRD.
Limitations of Medication for Treatment-Resistant Depression
Medication is often the first line of treatment for depression, but it may not be effective for everyone, particularly those with treatment-resistant depression. While antidepressant medications can help alleviate symptoms of depression, they may not work for several reasons.
Genetic Factors: Genetic differences can affect how an individual responds to antidepressant medications. Some people may have a genetic variation that makes it more difficult for the medication to work effectively.
Brain Chemistry: Depression is a complex condition that involves multiple neurotransmitters and brain regions. Antidepressant medications may not be able to fully address the underlying brain chemistry imbalances that contribute to depression.
Dose and Duration: The dosage and duration of antidepressant medication can impact its effectiveness. If the dosage is too low or the treatment duration is too short, the medication may not be able to fully address depressive symptoms.
Side Effects: Antidepressant medications can have side effects that may worsen depressive symptoms or make it difficult to tolerate the medication. Common side effects include nausea, headaches, and sexual dysfunction.
Comorbid Conditions: Individuals with treatment-resistant depression may have comorbid conditions, such as anxiety or substance use disorders, that can make it more challenging to find an effective treatment.
Understanding these limitations is crucial for individuals and healthcare providers to explore alternative and complementary treatment options for managing treatment-resistant depression.
Advanced Treatment Options for Treatment-Resistant Depression

For individuals with TRD, exploring innovative and evidence-based therapies can provide new hope. Here are some of the most effective options:
Ketamine Therapy
Ketamine is a groundbreaking treatment that has gained recognition for its ability to rapidly improve depressive symptoms in individuals with TRD. Administered as an IV infusion or esketamine nasal spray, ketamine works by targeting brain cells and restoring connections in areas of the brain involved in mood control. Benefits of ketamine therapy include:
Fast-acting relief (often within hours)
Effectiveness in reducing suicidal ideation
Positive outcomes for individuals who have not responded to standard treatments
Unlike traditional antidepressants, ketamine targets the glutamate system, offering a novel mechanism of action to tackle depression.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy is a non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic pulses to stimulate nerve cells in specific areas of the brain associated with mood regulation. TMS therapy is used for treating depression by specifically targeting the prefrontal cortex to help regulate mood. Approved by the FDA, TMS therapy is a safe and effective option for individuals with TRD. Key advantages include:
Minimal adverse effects compared to medications
Targeted treatment of brain areas involved in depression
Significant improvement in symptoms after several weeks of treatment
The procedure involves placing a magnetic coil on the scalp to deliver focused pulses to the prefrontal cortex, an area of the brain often underactive in people with depression.
Combination Therapies
In some cases, combining treatments like TMS and ketamine therapy can lead to a significant reduction in depressive symptoms. This approach allows for a more comprehensive management plan tailored to the individual’s needs. Additionally, therapies such as vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be considered for individuals with severe, persistent TRD.
Psychological Counseling and Talk Therapy
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, remains a cornerstone of depression treatment. When combined with other therapies, it helps individuals address underlying issues, develop coping strategies, and improve overall mental health. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy can offer targeted support to address the root causes of depression.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Treatment

In addition to advanced therapies, incorporating lifestyle changes can further improve symptoms of depression. Some effective strategies include:
Regular exercise: Promotes the release of endorphins, improving mood and energy levels
Healthy diet: Supports optimal brain function and overall well-being
Social support: Building connections with your friends, family, and/or support groups can reduce feelings of isolation whether you’re experiencing TRD or not.
Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness or yoga, to balance brain chemistry
Incorporating mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) or engaging in creative outlets like art or music therapy can further enhance emotional resilience. These changes, when combined with professional treatment, create a holistic approach to managing TRD.
Managing Treatment-Resistant Depression
Living with TRD can be challenging, but it is important to remain proactive and persistent in finding the right treatment. Here are some tips for managing the condition:
Work with a trusted healthcare provider: A mental health professional can help guide you through available treatment options.
Be open to trying new therapies: Advanced options like ketamine and TMS offer hope for individuals who haven’t found relief with conventional methods.
Focus on self-care: Prioritize sleep, nutrition, and stress management to support your overall health.
Seek support: Joining a support group or talking to others who understand your challenges can provide encouragement and motivation.
Track your progress: Keeping a journal of your symptoms, triggers, and responses to treatments can help you and your provider make informed decisions.
Finding Hope and Support
Treatment-resistant depression can feel overwhelming, but it is essential to remember that help is available. By working closely with a mental health professional and exploring advanced treatment options like ketamine therapy and TMS therapy, individuals with TRD can achieve lasting relief. Don’t lose hope—with the right treatment plan, it is possible to overcome the challenges of TRD and regain control over your life.
Overcoming Treatment-Resistant Depression
Overcoming treatment-resistant depression requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates multiple treatment strategies. Here are some steps that can help:
Seek Professional Help: Working with a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or therapist, is essential for developing an effective treatment plan. They can help identify the underlying causes of depression and recommend appropriate treatments.
Medication Adjustments: If antidepressant medications are not working, it may be necessary to try a different medication or combination of medications. A mental health professional can help determine the best course of treatment.
Therapy: Talk therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or interpersonal therapy (IPT), can be an effective adjunct to medication. Therapy can help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to depression.
Lifestyle Changes: Making healthy lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep, can help alleviate depressive symptoms.
Alternative Treatments: Alternative treatments, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), may be effective for individuals who have not responded to traditional treatments.
Support System: Building a support system of family, friends, and support groups can help individuals feel less isolated and more motivated to seek treatment.
By taking a comprehensive approach to treatment and seeking professional help, individuals with treatment-resistant depression can find relief from their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Contact Us

If you’re ready to explore advanced treatment options for mental health and wellness, we’re here to help. Contact PointHealth today:
Phone: 323-902-7489
Locations: Visit our locations page to find a clinic near you.
Our dedicated team is here to guide you toward a personalized treatment plan that works for you.